The start of a new decade brings with it new resolutions to improve one’s life, including adopting a healthier lifestyle. Here are 20 useful health tips to get you started on a healthier lifestyle in 2020.
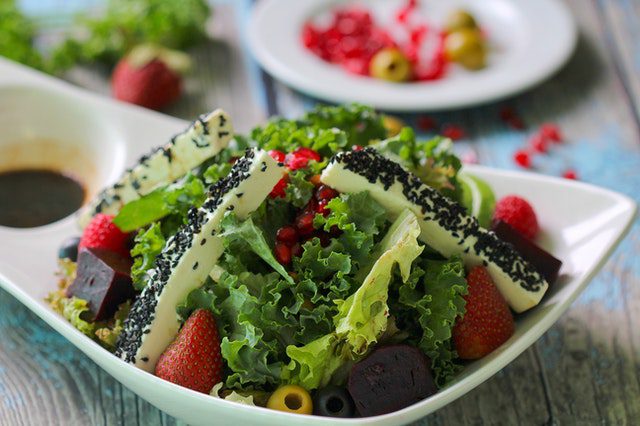
Maintain a nutritious diet.
Consume a wide range of foods, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and whole grains. Adults should eat at least five portions of fruits and vegetables per day (400g). Include fruits and vegetables in all of your meals, snack on fresh fruit and vegetables, eat a variety of fruits and vegetables and eat them in season to increase your intake. Eating healthy can reduce your risk of malnutrition and noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) such as diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and cancer.
Changing the diet should also be an option in order to improve health. Eating more healthy food, such as bbq chicken will improve your health and your life in general.
Reduce your consumption of salt and sugar.
Filipinos consume twice the recommended sodium intake, increasing their risk of hypertension and, as a result, heart disease and stroke. Salt is the most common source of sodium for most people. Limit your daily salt consumption to 5g, or about one teaspoon. In contrast, excessive sugar consumption raises the risk of tooth decay and unhealthy weight gain. In both adults and children, free sugar intake should be kept to less than 10% of total energy intake. For an adult, this is approximately 50g or 12 teaspoons. The WHO recommends consuming less than 5% of total energy intake for additional health benefits. Reduce your sugar intake by limiting your consumption of sugary snacks, candies, and sugar-sweetened beverages.
Reduce your consumption of unhealthy fats.
This will help to prevent unhealthy weight gain and NCDs. Fats come in a variety of forms, but unsaturated fats are preferred over saturated and trans fats. The World Health Organization recommends limiting saturated fat intake to less than 10% of total energy intake, trans fat intake to less than 1% of total energy intake, and replacing saturated and trans fats with unsaturated fats.
Saturated fats are found in fatty meat, butter, palm and coconut oil, cream, cheese, ghee, and lard; and trans fats are found in baked and fried foods, as well as pre-packaged snacks and foods such as frozen pizza, cookies, and biscuits.
Avoid drinking too much alcohol.
Alcohol consumption can lead to mental and behavioral disorders, as well as major NCDs like liver cirrhosis, some cancers, and heart disease, as well as injuries from violence and road rage.
Smoking should be avoided.
Tobacco use contributes to noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) such as lung disease, heart disease, and stroke. Tobacco kills both direct smokers and nonsmokers through second-hand smoke. Approximately 15.9 million Filipino adults currently smoke tobacco, but 7 out of 10 smokers are interested in or intend to quit.
It is not too late to quit smoking if you are a smoker. You will notice both immediate and long-term health benefits as a result. If you don’t smoke, that’s fantastic! Do not begin smoking in order to fight for the right to smoke-free air.
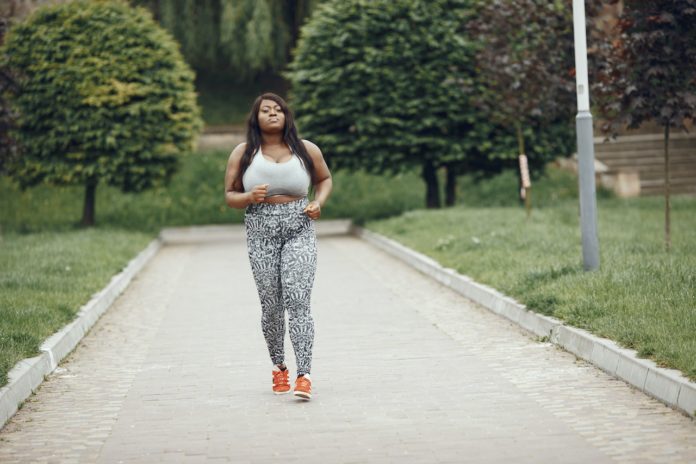
Take part in activities
Physical activity is defined as any bodily movement that necessitates the expenditure of energy by skeletal muscles. This includes physical activity and activities performed while working, playing, doing housework, traveling, and participating in recreational activities. Physical activity requirements vary by age group, but adults aged 18 to 64 should engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week. Increase moderate-intensity physical activity to 300 minutes per week to reap additional health benefits. This is very important for your health. A lot of people have fibromyalgia symptoms, which appears mainly because of inactivity.
Maintain a regular blood pressure check.
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, has earned the moniker “silent killer.” This is due to the fact that many people with hypertension are unaware of their condition because it has no symptoms. Regularly have your blood pressure checked by a health professional so you know what your numbers are. If your blood pressure is too high, consult a doctor. This is critical for the prevention and management of hypertension.
Get a vaccination
Vaccination is one of the most effective disease prevention methods. Vaccines protect you from diseases such as cervical cancer, cholera, diphtheria, hepatitis B, influenza, measles, mumps, pneumonia, polio, rabies, rubella, tetanus, typhoid, and yellow fever by working in tandem with your body’s natural defenses.
In the Philippines, free vaccines are distributed to children aged one and under as part of the Department of Health’s routine immunization program. You can ask your doctor to check your immunization status or have yourself vaccinated if you are an adolescent or an adult.
Cover your mouth when coughing or sneezing.
Diseases such as influenza, pneumonia, and tuberculosis are spread through the air. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, infectious agents can be spread to others via airborne droplets. When you start coughing or sneezing, cover your mouth with a face mask or tissue and dispose of it properly. When you cough or sneeze and don’t have a tissue nearby, use the crook (or inside) of your elbow to cover your mouth as much as possible.
Avoid being bitten by mosquitos.
Mosquitoes spread diseases like dengue fever, chikungunya, malaria, and lymphatic filariasis, all of which continue to affect Filipinos. To protect yourself and your loved ones from mosquito-borne diseases, simple precautions can be taken. If you are going to a place where mosquito-borne diseases are common, consult a doctor about getting a vaccine to prevent diseases like Japanese encephalitis and yellow fever, or if antimalarial medications are needed. Wear insect repellent and long-sleeved light-colored shirts and pants. Use window and door screens, bed nets, and clean your surroundings on a weekly basis to eliminate mosquito breeding sites at home.
Follow all traffic laws.
Every year, over one million people are killed in car accidents, and millions more are injured. A variety of government-enforced measures, such as stricter legislation and enforcement, safer infrastructure and vehicle standards, and improved post-crash care, can help to reduce road traffic injuries. You can also avoid road accidents by following traffic laws such as wearing a seatbelt for adults and a child restraint for your children, riding a motorcycle or bicycle with a helmet, not drinking and driving, and not using your cellphone while driving.
Drink only safe water.
Water-borne diseases such as cholera, diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid, and polio can be contracted by drinking contaminated water. At least 2 billion people around the world consume contaminated feces-contaminated water. To ensure the safety of the water you’re drinking, check with your water concessionaire and water refilling station. If you are unsure of your water source, boil it for at least one minute. This kills any potentially dangerous organisms in the water. Allow it to cool naturally before drinking.
Breastfeed your baby from birth to two years old and beyond.
Breastfeeding is the most effective way to provide newborns and infants with optimal nutrition. According to WHO, breastfeeding should begin within one hour of birth. Breastfeeding is essential for the baby’s health during the first six months. Breastfeeding should be continued for at least two years and possibly for a longer period of time. Breastfeeding benefits both the mother and the baby by lowering the risk of breast and ovarian cancer, type II diabetes, and postpartum depression.
Talk to people you trust in case you’re feeling down.
Depression is a common disease that affects more than 260 million people worldwide. Depression can manifest in a variety of ways, including feelings of hopelessness or worthlessness, as well as frequent negative and disturbing thoughts or an overwhelming sense of pain. Talk to someone you trust about your feelings, such as a family member, friend, colleague, or mental health professional.
Antibiotics should only be used as directed.
Antibiotic resistance is one of the most serious public health threats of our time. Bacterial infections become more difficult to treat when antibiotics lose their effectiveness, resulting in higher medical costs, longer hospital stays, and higher mortality. Because of human and animal misuse and overuse, antibiotics are losing their effectiveness. Antibiotics should only be taken if prescribed by a qualified health professional. And, once prescribed, strictly adhere to the treatment schedule. Antibiotics should never be given to others.
Clean your hands thoroughly.
Hand hygiene is important for everyone, not just health professionals. Keeping your hands clean can help keep infectious diseases at bay. Handwash with soap and water or rub your hands with an alcohol-based product if your hands are visibly soiled.
Prepare your food properly.
These diseases include everything from diarrhea to cancer. When purchasing food at the market or store, check the labels or the actual product to ensure it is safe to eat. When preparing food, remember the Five Keys to Safer Food: (1) maintain cleanliness; (2) separate raw and cooked foods; (3) thoroughly cook; (4) keep food at safe temperatures; and (5) use safe water and raw materials.
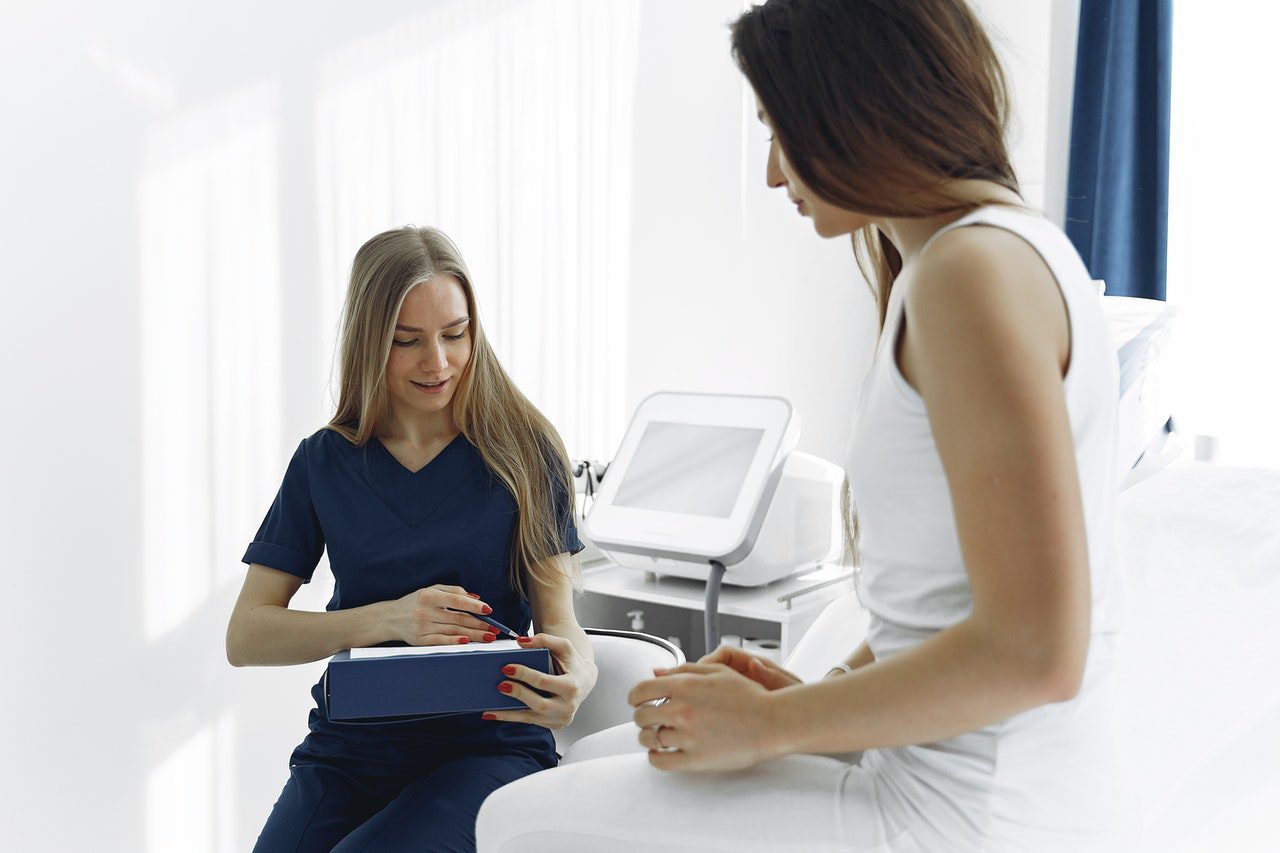
Plan regular check-ups.
Regular check-ups can aid in the detection of health problems before they become serious. Health professionals can help detect and diagnose health issues early on, when treatment and cure are more likely. Visit your neighborhood health center to learn about the health services, screenings, and treatments that are available to you.